Expansion Cards
$20.00
Expansion cards are hardware components installed into a computer’s motherboard slots to add or enhance system functionality, such as graphics, sound, network, or storage capabilities.
Expansion cards are one of the most important components in modern computing, designed to extend the functionality of a computer beyond what is offered by the motherboard alone. From the earliest days of personal computers, users and businesses have relied on expansion cards to customize and upgrade systems according to their specific needs. Whether you are a gamer demanding high-end graphics, a professional requiring advanced audio processing, or an IT administrator looking to boost network performance, expansion cards make it possible to tailor a computer to fit those requirements.
What Are Expansion Cards?
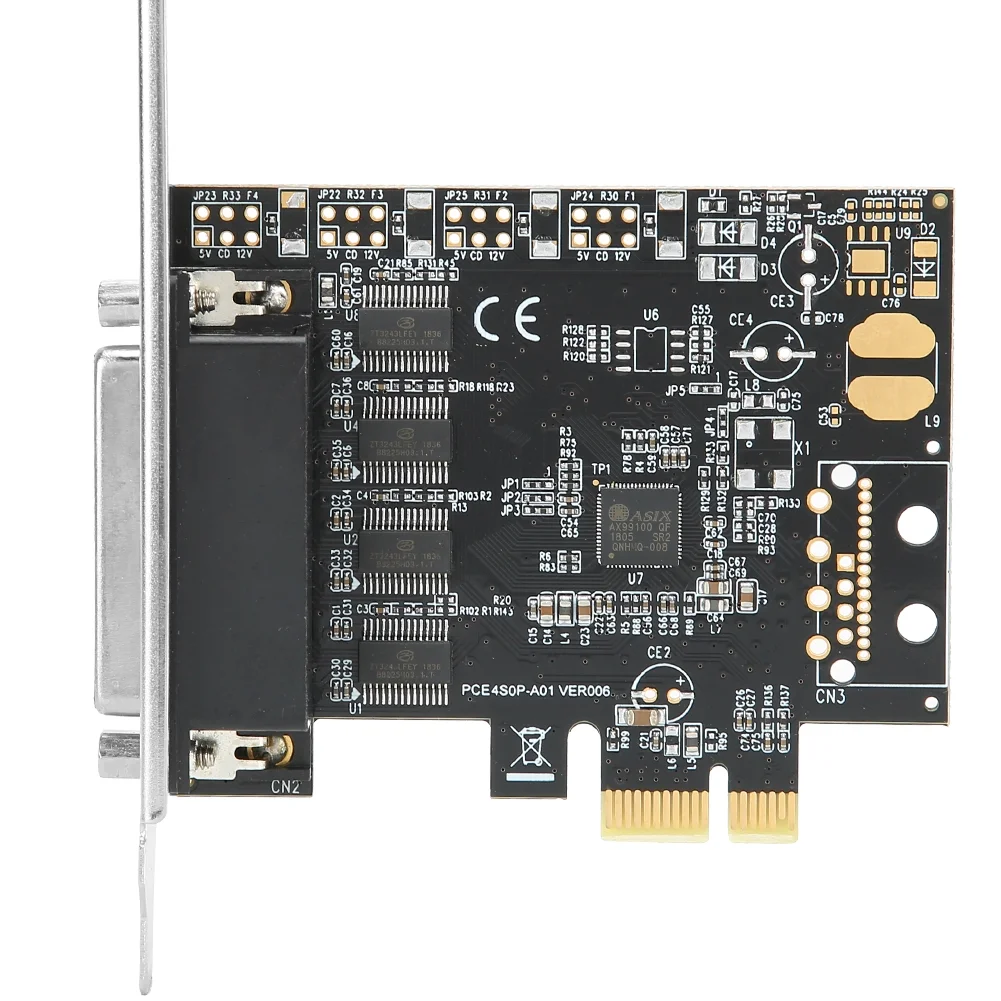
Expansion cards, sometimes called add-on cards or adapter cards, are printed circuit boards that fit into an expansion slot on the motherboard. These slots, typically based on standards such as PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect), PCI Express (PCIe), or older formats like AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) and ISA (Industry Standard Architecture), allow direct communication between the card and the rest of the computer’s components.
When installed, expansion cards provide additional hardware capabilities that are not integrated into the motherboard. For example, most motherboards come with basic onboard graphics and audio. However, for tasks like professional video editing, 3D rendering, or high-performance gaming, specialized graphics and sound cards deliver far superior results.
Types of Expansion Cards
Graphics Cards (GPU Cards)
Perhaps the most well-known expansion cards, graphics cards are essential for visual output. While integrated graphics are enough for everyday computing, a dedicated GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can handle demanding applications such as video games, CAD software, 3D modeling, and artificial intelligence.
Modern GPUs, like those from NVIDIA and AMD, feature massive processing power, dedicated video memory, and advanced cooling solutions.
Sound Cards
Sound cards enhance audio quality beyond what integrated solutions provide. They are crucial for audiophiles, musicians, and video editors who require studio-grade recording and playback.
Advanced sound cards support surround sound systems, higher sampling rates, noise reduction, and specialized inputs for instruments and microphones.
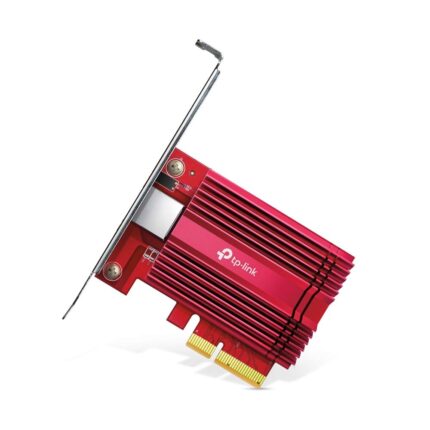
Network Interface Cards (NICs)
Network cards enable computers to connect to networks and the internet. While most motherboards now come with built-in Ethernet and Wi-Fi, dedicated NICs are used for faster speeds, better reliability, and special features like server optimization, low latency, and dual-port connections.
Storage Controller Cards
These cards manage storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) controller cards are widely used in servers and high-performance workstations to improve speed, reliability, and data redundancy.
Capture Cards
Popular with gamers, content creators, and broadcasters, capture cards allow users to record or stream video from external devices such as gaming consoles, cameras, or another PC.
TV Tuner Cards
These cards enable computers to receive television signals. Although less common today due to streaming services, TV tuner cards are still used in specialized environments.
Modem Cards
Before broadband and fiber internet became widespread, modem cards were used for dial-up connections. While mostly obsolete now, they played an essential role in the history of networking.
How Expansion Cards Work
Expansion cards communicate with the CPU and system memory through the motherboard’s bus interface. The most widely used standard today is PCI Express (PCIe). PCIe provides different lanes (x1, x4, x8, x16), and the number of lanes determines bandwidth and performance. For instance, a graphics card typically uses a PCIe x16 slot to maximize data throughput, while a network or sound card may only require a smaller x1 slot.
Each card contains its own processors, chips, and memory (if required). This means that rather than relying solely on the CPU, expansion cards perform specialized tasks independently, leading to greater efficiency and better overall performance.
Benefits of Expansion Cards
Customizability
Users can upgrade their systems without replacing the entire computer. Need better graphics? Add a new GPU. Want enhanced connectivity? Install a new NIC.
Performance Boost
Specialized hardware outperforms integrated components, delivering higher speeds, better graphics rendering, or improved audio clarity.
Longevity of Systems
Instead of buying a completely new system, businesses and individuals can extend the useful life of existing hardware with expansion cards.
Special Features
Some cards offer features not available on standard motherboards, such as hardware-based video encoding, multi-GPU support, or advanced surround sound.
Expansion Cards vs. Integrated Components
Modern motherboards are equipped with many integrated features. However, integrated solutions are often “good enough” for basic use but limited in high-demand scenarios. For example:
Integrated graphics can handle video playback but struggle with 3D gaming.
Built-in audio may suffice for casual listening but lacks the depth and clarity required for professional mixing.
Onboard network adapters usually cap out at gigabit speeds, whereas dedicated NICs can provide 10Gbps or higher.
Thus, expansion cards remain crucial for enthusiasts, professionals, and businesses that require superior performance.
Installation Process
Installing an expansion card is relatively straightforward:
Power down the computer and unplug it.
Open the case and locate the appropriate expansion slot.
Remove the protective slot cover on the case.
Carefully insert the expansion card into the slot, ensuring it is firmly seated.
Secure the card with a screw or latch.
Connect any additional power cables if needed (especially for GPUs).
Close the case, power on the computer, and install necessary drivers.
Future of Expansion Cards
As computing technology advances, the role of expansion cards continues to evolve. With the rise of AI, VR, and 8K video editing, the demand for high-performance GPUs and storage controllers is stronger than ever. Similarly, as networks adopt 10Gbps, 40Gbps, and even 100Gbps speeds, NICs will continue to play a vital role in enterprise environments.
Meanwhile, many consumer devices are trending toward integration and portability (e.g., laptops, tablets), which often limits expansion. However, innovations such as external GPUs (eGPUs) and Thunderbolt expansion docks are bridging the gap, giving portable devices desktop-like performance when needed.
Conclusion
Expansion cards are the backbone of computer customization and performance enhancement. They allow users to shape their machines according to unique needs, whether for gaming, professional media creation, high-speed networking, or enterprise-level storage management. While integrated components have grown more capable over the years, expansion cards remain irreplaceable in scenarios where power, precision, and flexibility are required.
In short, expansion cards transform an ordinary computer into a specialized powerhouse, ensuring technology can evolve alongside the ever-changing demands of its users.
Fast Dispatch – Orders are processed within 24–48 hours after confirmation.
Secure Packaging – All products are packed safely to avoid damage during shipping.
Estimated Delivery – Standard delivery usually takes 3–7 business days depending on your location.
Tracking Available – Once your order is shipped, you’ll receive a tracking link via email/SMS.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.